3.1.3.6 R&D for the energy transition
At end 2021, EDF’s R&D employed 1,784 people in France representing 30 nationalities. Among electricity suppliers, it has one of the largest R&D budgets, mostly devoted to energy and climate transition.
Breakdown of R&D investments by technology
99% of EDF R&D’s operating budget in France is dedicated to decarbonation and the energy systems transition. In particular, expenditures covered energy efficiency, uses of electricity as a substitute for fossil fuels, renewable energies and their insertion into the grid, energy production and storage, low-carbon hydrogen and its applications for decarbonising the economy, the local impacts of climate change and other environmental issues such as biodiversity, water quality, and the mitigation of disturbances. Nuclear power accounts for 43% of EDF R&D; renewable energies account for 14%.
Example: work on LCAs (LifeCycle Analyses)
To identify solutions with the smallest environmental impacts, EDF R&D teams are performing lifecycle analyses of the various processes used to produce electricity and hydrogen, and uses of kWh (electric mobility, buildings, batteries).
According to the IPCC (1), greenhouse gas emissions based on a lifecycle approach for one electrical kWh produced by a nuclear facility are 12g/kWh, compared to wind turbine (on-shore) and photovoltaic solar segments which respectively have a carbon footprint of 11g/kWh and 44g/kWh (see section 1.5 “Research and development, patents and permits”).
This has resulted in the most recent reference study of the LCA for each kWh produced by the French nuclear fleet (4gCO2eq/kWh, determined in 2000) being revised to incorporate changes in methods and the new data available (work in progress).
3.1.3.7 Innovation supporting the energy transition
The energy transition involves exploring innovative solutions. This is the aim of the EDF Pulse ecosystem (see section 3.3.3.6.6 “Developing a culture of innovation: the EDF Pulse ecosystem”).
3.1.4 Developing sobriety in electricity uses and innovative energy services
| A key source of leverage for decarbonisation |
With largely low-carbon electricity, the development of uses of low-energy, innovative electricity uses and services is a key vector for work to combat global warming. |
| Developing appropriate offerings |
The EDF group is contributing to this goal by means of offers tailored to various markets, including promoting the use of heat pumps, electric mobility, and energy efficiency solutions. See section 3.1.4.3 “Developing efficient, low-energy, innovative energy services”. |
| Establishing the conditions for the development of effective, low-energy uses |
Electrifying sectors that produce the most CO2 entails having conditions that are favourable to this development. See section 3.1.4.2 “Setting the conditions for the efficient development of electricity uses”. |
3.1.4.1 Commitment to supporting customer decarbonisation
One of the key indicators in combatting global warming is the quantity of CO2 emissions avoided.
To date, there is no recognised external reference that can be used to determine the amount of emissions avoided by customers thanks to the products and services EDF sells. However, EDF can follow principles for such calculations according to the most frequently observed practices in this respect. At the same time, EDF is engaged in French and international research seeking to develop this type of benchmarking method.
In 2021, EDF calculated emissions avoided by the following products and services sold by EDF and Dalkia: developing renewable energies in heat networks, energy efficiency at thermal facilities, photovoltaic production (installations sold to customers and self-consumption, not including EDF installations reinjecting their production into the network), electric mobility, residential heat pumps. The indicator corresponds to the gap in emissions from the product or service sold and emissions in a baseline scenario established for each product or service. For the methods used for this indicator, see section 3.6 “Methodology”. Extension to other EDF group entities (UK, Italy, and Belgium) and, potentially, other products and services, is being examined.
The 2021 results cover only some of the products and services marketed by EDF. The figures should increase in the coming years, subject to possible changes in method in order to remain in line with third-party practices.
Avoided CO2 emissions thanks to sales of innovative goods and services (MtCO2)
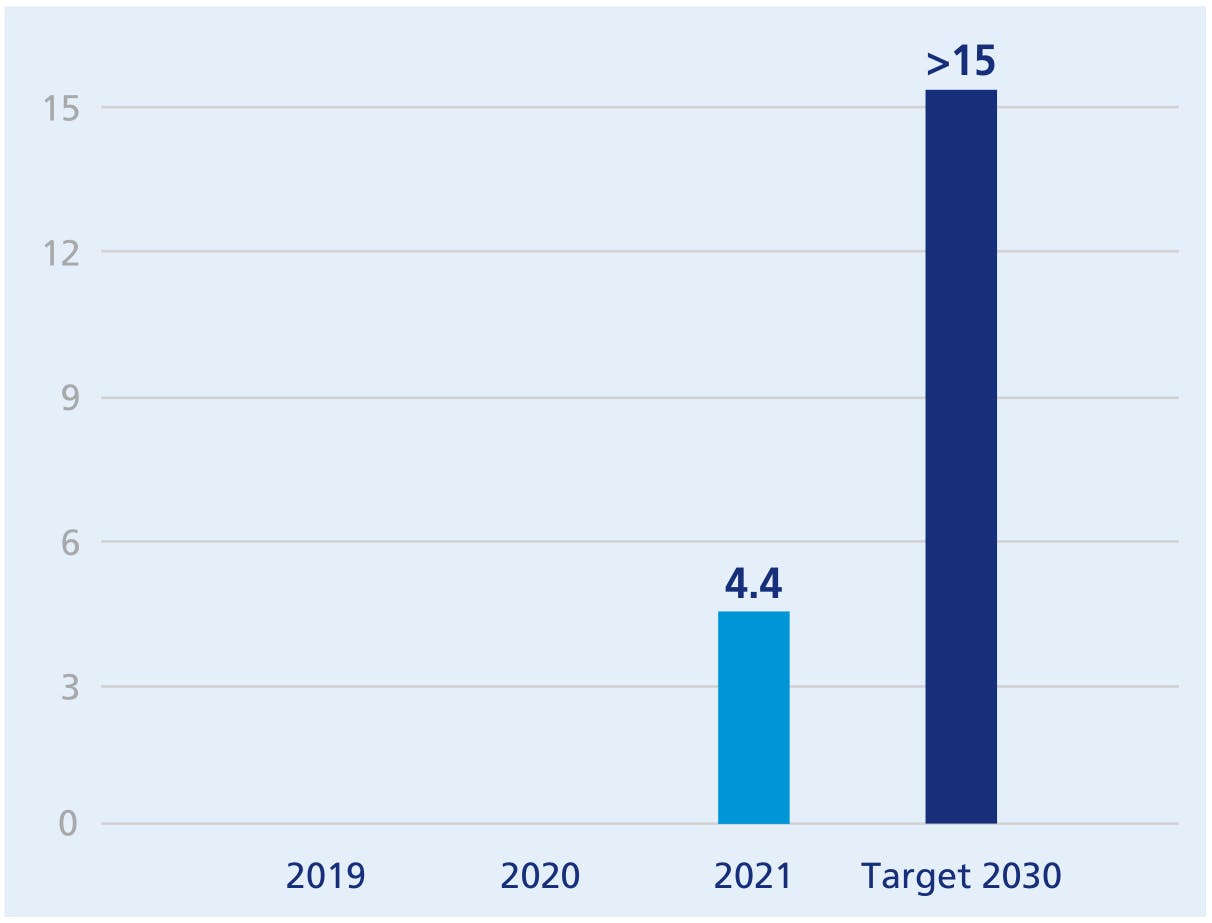
This graph shows us the CO2 emissions avoided thanks to the sale of innovative products and services (in MtCO2).
2019 :
2020 :
2021 : 4.4
Target 2030 : > 15
(1) IPCC Assessment report 5, 2014, Working Group III Mitigation of Climate Change, Annex III, Table A.III.2 (Emissions of selected electricity supply), medium values.
